vSAN 7 Update 1 What (Else) is new – Networking
I figured I’d cover in a blog some of the less obvious changes in vSAN 7 Update 1.
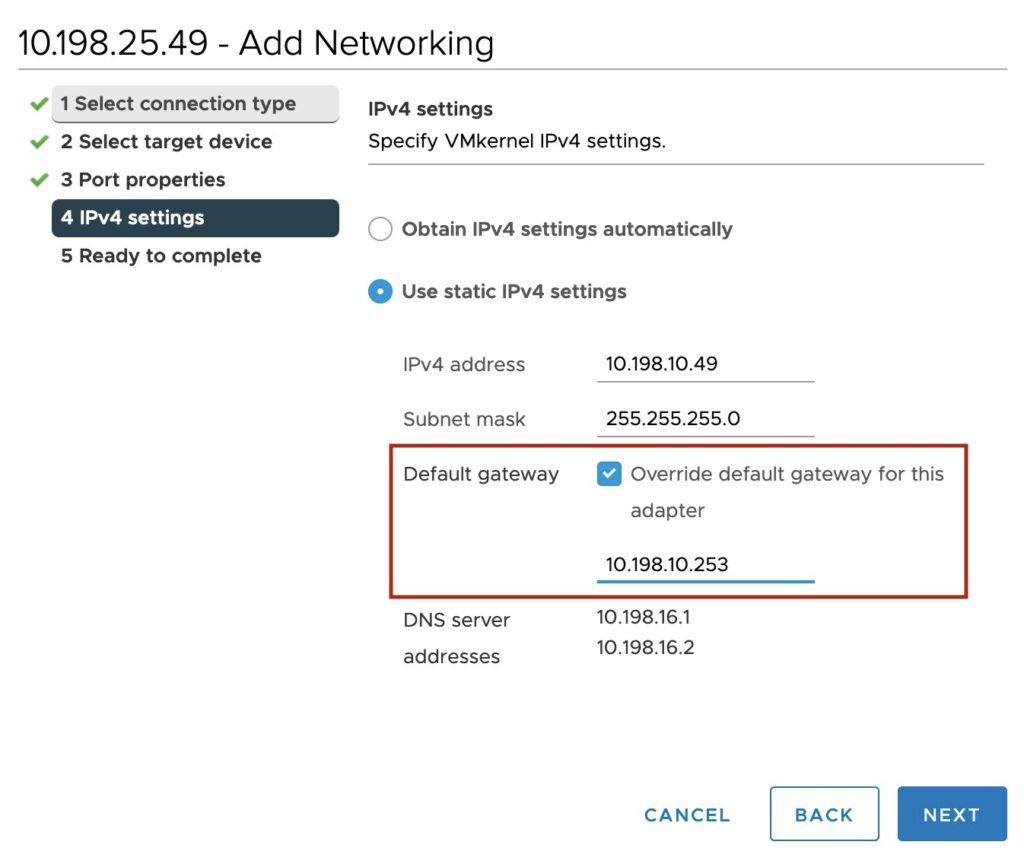
Simplified Layer 3 – vSAN has supported layer 3 (hosts within a cluster being on different subnets) since the early days. This is a popular topology when using stretched clustering, and 2 node configurations. vSAN VMkernel ports share the same gateway setting specified for the management network. As the vSAN network (ideally) often on a completely different subnet, this means that a static route would need to be set on each host. To simplify alternative gateway configuration, the vCenter Server UI now supports overriding the default gateway for a VMkernel port. ESXCLI or PowerCLI can still configure a gateway (there’s even now a ESXCLI -g flag to set a default gateway).
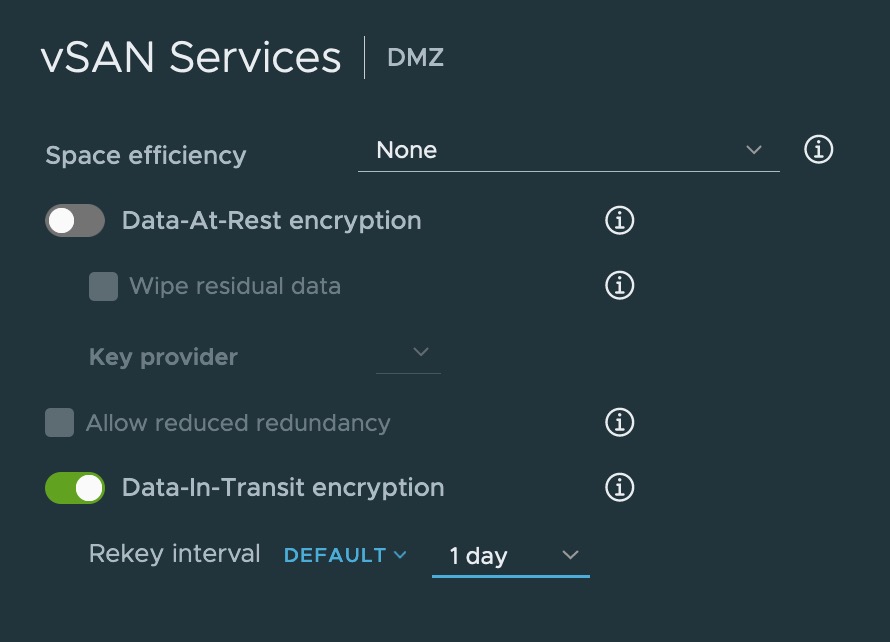
Data-In-Transit encryption – historically the focus on storage transport security was focused on restricting access to the storage networks (dedicated VLANs for Ethernet, or hard zoning for Fibre Channel) or limited authentication and access filtering (NFS IP ACL, IQN filteriing, CHAP, Soft zoning). If an adversary could capture the frames in transit on the storage network none of these technologies (or even data at rest encryption) protected you from data exfiltration. To address this, vSAN now supports data in transit encryption. This leverages the FIPS 140-2 validated Cryptographic modules to encrypt vSAN network traffic in flight. this allows custom rekey windows (The default is 1 day). No KMS is required for this solution to be deployed, and this feature complements other VMware in flight encryption technology (encrypted vMotion, encrypted HCX/NSX tunnels etc) so you can now encrypt all the things.
General Performance and monitoring improvements
As customers move to 25Gbps and 100Gbps switching, further optimizations have been made to the networking stack to increase parallelization of the CPU threads used for networking transport, increasing the efficiency this parallelizations balancing of and reduce overall CPU consumption per thread. These benefits will be most pronounced with RAID 5/6 usage, and multiple disk groups.
Networking monitoring improvements have been made to the vSAN network health checks. This will result in faster, more accurate automated network testing.

